UV and ozone secondary sanitizers use light and oxygen molecules to quickly and chemically-free kill bacteria, viruses, and other germs. UV-C light damages microbes’ DNA, while ozone reacts with their cell components. UV is ideal for surfaces, and ozone can reach hard-to-access areas like air and water. Both options are effective but require proper safety measures and maintenance. To understand how these powerful sanitizers work and their best uses, keep exploring further.
Key Takeaways
- UV and ozone are chemical-free secondary sanitizers that rapidly inactivate microorganisms on surfaces, air, and water.
- UV-C light damages microbial DNA/RNA, while ozone oxidizes cell components to kill pathogens.
- UV is effective on exposed surfaces, whereas ozone can reach hard-to-access areas and purify air and water.
- Both require proper safety measures: UV can harm skin/eyes, and ozone inhalation may cause respiratory issues.
- Regular maintenance and correct usage are essential for maximizing their disinfection effectiveness and safety.
How UV and Ozone Sanitizers Work

UV and ozone sanitizers work by using specific types of energy to destroy harmful microorganisms. When you turn on a UV or ozone sanitizer, it emits ultraviolet light or ozone molecules that penetrate cell walls of bacteria, viruses, and fungi. The UV light damages their DNA or RNA, preventing replication and rendering them inactive. Ozone, a powerful oxidizer, reacts with cell components, breaking down their structure and killing the microorganisms. These processes happen rapidly, often within seconds to minutes, providing effective disinfection without chemicals or physical scrubbing. You don’t need to use harsh cleaners or touch surfaces directly—just expose the items or areas to the sanitizer. This method guarantees a thorough, chemical-free way to sanitize surfaces, air, or water efficiently. Mazda Tuning techniques can also optimize vehicle air quality systems for better sanitation. Understanding sterilization methods highlights the importance of using energy-based technologies like UV and ozone for safe and effective disinfection. Additionally, understanding the regional flavors and traditions can enhance the appreciation of regional culinary arts during sanitization processes, especially in food-related environments. Proper surface disinfection techniques are essential to ensure complete elimination of pathogens and prevent cross-contamination. Incorporating advancements in AI technology can help in monitoring and optimizing sanitation procedures for improved safety and efficiency.
Types of UV Light Used in Sanitization
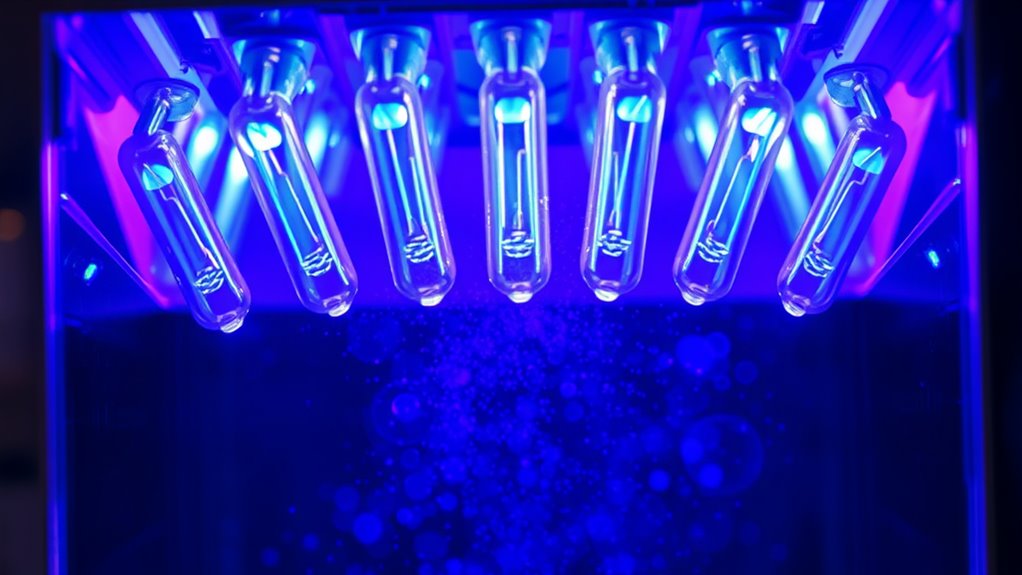
Different types of UV light are employed in sanitization devices to target microorganisms effectively. The most common is UV-C, which has wavelengths between 200 and 280 nanometers. UV-C is highly effective at damaging the DNA and RNA of bacteria, viruses, and fungi, rendering them inactive. Some devices also use UV-B or UV-A, but these are less effective for sterilization purposes. UV-C lamps are typically mercury vapor lamps that emit a strong, germicidal wavelength. Recent advancements include LED-based UV-C lights, which are more energy-efficient and have a longer lifespan. When selecting a sanitizer, make sure it uses UV-C light specifically, as this is the most proven for disinfection. Proper exposure time and distance are vital to guarantee effective sterilization. Understanding UV-C’s effectiveness is essential for maximizing sanitization results. Additionally, the safety precautions necessary during UV-C operation help prevent potential skin and eye damage. Using UV-C safety gear such as protective glasses and gloves can further reduce risks. Incorporating UV-C technology into sanitization routines can significantly enhance pathogen elimination efficiency. A thorough understanding of the different UV wavelengths and their specific properties can help optimize sanitization strategies.
The Role of Ozone in Disinfection

Have you ever wondered how ozone contributes to effective disinfection? Ozone is a powerful oxidizer that destroys bacteria, viruses, and other pathogens by breaking down their cell walls. When you expose surfaces or water to ozone, it reacts quickly, neutralizing contaminants on contact. Unlike other sanitizers, ozone doesn’t leave harmful residues, making it environmentally friendly. It also penetrates hard-to-reach areas, ensuring thorough disinfection. You’ll find ozone used in water treatment, air purification, and surface sterilization because of its effectiveness. Its ability to rapidly oxidize organic matter makes it a reliable secondary sanitizer, especially when combined with other methods. Additionally, the use of ozone aligns with privacy policies by avoiding the need for chemical residues that could raise health concerns. By generating ozone, you enhance your disinfection process, reducing microbial presence without relying solely on chemical disinfectants.
Comparing Effectiveness: UV vs. Ozone

When comparing UV and ozone for disinfection, you’ll notice differences in their germicidal capabilities and practicality. UV light effectively neutralizes many pathogens quickly, but ozone can reach areas UV can’t access. Consider safety aspects and ease of use to determine which method best fits your needs. Additionally, hyundai tuning techniques can optimize vehicle performance, much like choosing the right disinfection method enhances safety. Understanding engine tuning options can help you improve your vehicle’s efficiency and power, making maintenance more effective and tailored to your driving style. Incorporating biodiversity benefits into your decision-making can also ensure environmentally friendly practices are considered alongside disinfection efficiency. Recognizing the environmental impact of each method can guide more sustainable choices in your disinfection strategy. Moreover, selecting appropriate planters can influence the overall effectiveness of indoor gardening, reflecting the importance of suitable tools in achieving optimal results.
Germicidal Capabilities Comparison
UV light and ozone are both effective secondary sanitizers, but they work in fundamentally different ways to eliminate germs. UV light destroys microorganisms by damaging their DNA or RNA, preventing replication. Ozone, on the other hand, oxidizes cell walls and internal structures, killing bacteria and viruses through chemical reactions. When comparing their germicidal capabilities, consider these points:
- UV is rapid, acting within seconds to minutes, ideal for quick disinfection.
- Ozone provides broader coverage, especially in hard-to-reach areas.
- UV is most effective on surfaces directly exposed to light.
- Ozone can disinfect air, water, and surfaces simultaneously, penetrating crevices and shadows.
- Proper tuning of UV and ozone devices ensures maximum germicidal efficiency and safety in various environments.
Both are powerful, but their suitability depends on your specific sanitizing needs and environment.
Safety and Practicality
Both UV light and ozone are effective sanitizers, but their safety and practicality vary considerably. UV light is generally safe when used correctly, as it doesn’t leave harmful residues and operates quickly. However, direct exposure can harm your skin and eyes, so precautions are necessary. Proper UV exposure protocols are essential to ensure safety during use. Ozone, on the other hand, is potent but can pose health risks if inhaled in high concentrations, causing respiratory issues. Its application requires careful control and proper ventilation, making it less convenient for everyday use. UV systems are often more straightforward to implement indoors, while ozone treatments are better suited for controlled environments or industrial settings. Overall, UV offers greater safety and ease of use, whereas ozone’s strength demands more careful handling. Additionally, understanding the best beaches can help you choose safe environments for outdoor ozone or UV treatments when visiting coastal areas. Considering the types of sanitizers available can further assist in selecting the most appropriate method for your needs. Furthermore, evaluating the effectiveness in different settings can guide users in making informed decisions based on their specific requirements. The regulations surrounding ozone use also vary by region, which can impact how and where it is safely applied.
Applications of UV and Ozone Sanitizers

UV and ozone sanitizers are increasingly applied across various industries to guarantee safety and hygiene. You’ll find them in healthcare, water treatment, food processing, and HVAC systems, where they effectively reduce bacteria, viruses, and other contaminants. These sanitizers are valued for their chemical-free disinfection and quick action, making them ideal for sensitive environments. Implementing regular assessment and maintenance ensures optimal performance and longevity of these sanitizing systems. Additionally, understanding the vibrational energy involved can enhance the effectiveness of these technologies in achieving thorough sterilization.
Safety Considerations and Precautions

While UV and ozone sanitizers are highly effective, they can pose health risks if not used properly. UV light can cause skin burns and eye injuries if you look directly at it, so always operate devices with protective covers and avoid exposure during use. Ozone, when inhaled in high concentrations, can irritate your respiratory system and worsen asthma symptoms. Ensure proper ventilation in the area during and after use to prevent ozone buildup. Follow manufacturer instructions carefully, including recommended exposure times and safety precautions. Never modify or bypass safety features. Keep children and pets away from sanitizing devices. Regularly inspect equipment for damage, and store it in a secure, dry location when not in use. Safety first safeguards your health and the effectiveness of the sanitizing process.
Benefits of Using Secondary Sanitizers

Secondary sanitizers substantially enhance overall hygiene by providing an extra layer of protection beyond primary cleaning methods. They help eliminate bacteria, viruses, and mold that might survive initial cleaning, ensuring a higher level of cleanliness. Using secondary sanitizers can reduce the risk of cross-contamination and keep environments safer. Additionally, they can extend the lifespan of your primary sanitization systems by supporting ongoing disinfection.
Secondary sanitizers provide an extra layer of protection, eliminating residual bacteria, viruses, and mold for safer, cleaner environments.
Here are some benefits:
- Boosts overall hygiene effectiveness
- Minimizes microbial presence
- Supports ongoing sanitation efforts
- Reduces risk of infections and illnesses
Incorporating secondary sanitizers into your routine ensures thorough cleanliness, giving you peace of mind and a healthier environment. They’re an essential addition to maintaining high standards of hygiene in various settings.
Limitations and Potential Risks

Despite their benefits, secondary sanitizers like UV and ozone systems come with limitations and potential risks that you should consider. UV light isn’t effective against all pathogens, especially those shielded by debris or biofilms, so it might not sanitize thoroughly if surfaces are dirty. Ozone, while powerful, can cause respiratory issues if not handled properly, and high concentrations may damage rubber and certain plastics. Both systems require proper maintenance; neglect can reduce their effectiveness and introduce health hazards. Overusing ozone might lead to lingering odors or irritate your respiratory system. Additionally, UV systems need direct exposure; shadows or obstructions weaken their performance. Recognizing these risks helps you use secondary sanitizers safely and effectively, ensuring you achieve sanitation without unintended consequences.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Long Do UV and Ozone Sanitizers Typically Last?
You’re wondering how long UV and ozone sanitizers last. Generally, UV bulbs last about 9,000 to 10,000 hours of use, which translates to roughly a year or two depending on usage. Ozone generators tend to have a longer lifespan, often around 3 to 5 years if properly maintained. Regular cleaning and following manufacturer instructions will help prolong their effectiveness and ensure you get the most out of your sanitizers.
Are There Environmental Impacts From Using UV and Ozone Sanitizers?
You might wonder if using UV and ozone sanitizers harms the environment. While they effectively kill germs, UV light consumes minimal energy, and ozone dissipates quickly, leaving no harmful residues. However, ozone can be a respiratory irritant if not properly managed, so using these devices responsibly minimizes environmental impact. Overall, they’re eco-friendlier options compared to chemical sanitizers, but caution guarantees you don’t accidentally cause air quality issues.
Can UV and Ozone Sanitizers Be Used Together Effectively?
You’re wondering if UV and ozone sanitizers can team up effectively. The answer is yes, when used properly, they complement each other well. UV light disrupts microorganisms’ DNA, while ozone breaks down organic contaminants. Together, they provide a double whammy for sanitation. Just keep in mind, coordination is key—using them simultaneously or sequentially requires careful planning to maximize benefits and minimize any potential safety concerns.
What Maintenance Is Required for UV and Ozone Sanitizing Devices?
You need to regularly clean and inspect your UV and ozone sanitizing devices. Replace UV bulbs according to the manufacturer’s schedule, usually annually, and verify they’re functioning properly. Check ozone generators for leaks or damage, and clean filters as needed. Keep vents clear for proper airflow, and follow any specific maintenance instructions provided. Regular upkeep ensures your devices operate efficiently and continue to effectively sanitize your environment.
Do UV and Ozone Sanitizers Work on All Types of Pathogens?
You might wonder if UV and ozone sanitizers work on all pathogens. In general, UV light effectively inactivates bacteria, viruses, and fungi by damaging their DNA or RNA. Ozone is a strong oxidizer that destroys many bacteria and viruses by disrupting their cell walls. However, neither is universally effective against all pathogens, especially those with protective spores or embedded in complex matrices. Always check if your sanitizer is rated for specific microorganisms you aim to target.
Conclusion
Now that you understand how UV and ozone sanitizers work, you can see their powerful role in disinfecting your space. They’re effective, safe when used properly, and versatile for various applications. But have you considered how much cleaner your environment could be with these advanced solutions? By choosing the right secondary sanitizer, you’re taking a smart step toward a healthier, germ-free environment. Are you ready to make that safer, cleaner choice today?









